quadratic equations (introduction)
In elementary algebra, a quadratic equation (from the Latin quadratus for "square") is any equation having the form
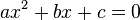
where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c are constants with a not equal to 0. If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic. The constants a, b, and c are called, respectively, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant or free term.
source: youtube.com
No comments:
Post a Comment